Rat Interleukin-4 Recombinant
Categories: HematopoietinsIL-2 familyRecombinant Rat Cytokines$70.00 – $4,700.00
Description
Accession
P20096
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding Rat Interleukin-4 mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
Native Rat Interleukin-4, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide,the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 14 kDa. Recombinant Interleukin-4 is a monomer protein consisting of 126 amino acid residue subunits, migrates as an approximately 14 kDa protein under reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>98%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
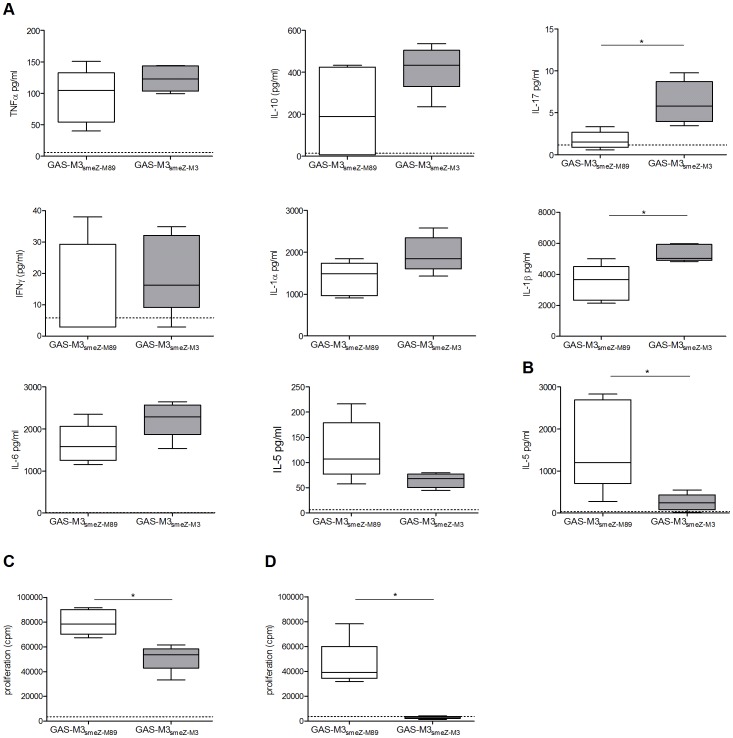
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation of human TF-1 cells is ≤.4 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of ≥x units/mg.
Protein Sequence
MGLSPHLAVT LFCFLICTGN GIHGCNDSPL REIINTLNQV TEKGTPCTEM FVPDVLTATR NTTENELICR ASRVLRKFYF PRDVPPCLKN KSGVLGELRK LCRGVSGLNS LRSCTVNEST LTTLKDFLES LKSILRGKYL QSCTSMS
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant IL-4was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered PBS solutionpH.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Biological Process
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
DC generation
- Study was approved by the IRB of the Charles University, 2nd Medical School.
- Immature monocyte-derived DCs were generated as previously described [2 culture flasks .
- 1 × 107 adherent monocytes were cultured for 5 days in culture media in the presence of GM-SF at the concentration of 500U/ml and 20 ng/ml ofL-4 [5 D/ml and activated using Poly at 25 μg/ml, LPS at 1 μg/ml, or a cocktail of proinflammatory cytokines (L-1 andL-6, ).
- Immature and mature DCs were used for further studies.
Adoptive transfer of cultured T cells
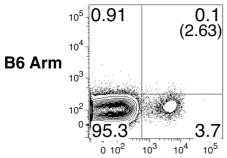
- Spleens and lymph nodes (axillary and cervical) were collected from C57BL/6J female mice.
- The spleens were mechanically disrupted, washed twice, and resuspended in cold PBS.
- The lymph nodes were also mechanically disrupted and incubated on ice for 5 min followed by collection of the supernatant and centrifugation at 1400 r.p.m.
- The pellet was then suspended in cold PBS.
- These samples were filtrated with a 70-
μ m Cell Strainer and suspended in medium'>medium'>RPMI medium'>1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 IU/ml penicillin, 100μ g/ml streptomycin, 1μ M sodium pyruvate, and 2.5μ Mβ -mercaptoethanol (medium'>medium'>RPMI growth medium). - CD4+ T cells were isolated by magnet sorting with anti-CD4 magnet beads according to the manufacturer's instructions .
- CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3ɛ/anti-CD28 antibodies coated on 24-well plates at a concentration of 5
μ g/ml each. - Th1-conditioned cells were differentiated by the addition of…
Adoptive transfer of cultured T cells
- Spleens and lymph nodes (axillary and cervical) were collected from C57BL/6J female mice.
- The spleens were mechanically disrupted, washed twice, and resuspended in cold PBS.
- The lymph nodes were also mechanically disrupted and incubated on ice for 5 min followed by collection of the supernatant and centrifugation at 1400 r.p.m.
- The pellet was then suspended in cold PBS.
- These samples were filtrated with a 70-
μ m Cell Strainer and suspended in medium'>medium'>RPMI medium'>1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 IU/ml penicillin, 100μ g/ml streptomycin, 1μ M sodium pyruvate, and 2.5μ Mβ -mercaptoethanol (medium'>medium'>RPMI growth medium). - CD4+ T cells were isolated by magnet sorting with anti-CD4 magnet beads according to the manufacturer's instructions .
- CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3ɛ/anti-CD28 antibodies coated on 24-well plates at a concentration of 5
μ g/ml each. - Th1-conditioned cells were differentiated by the addition of…
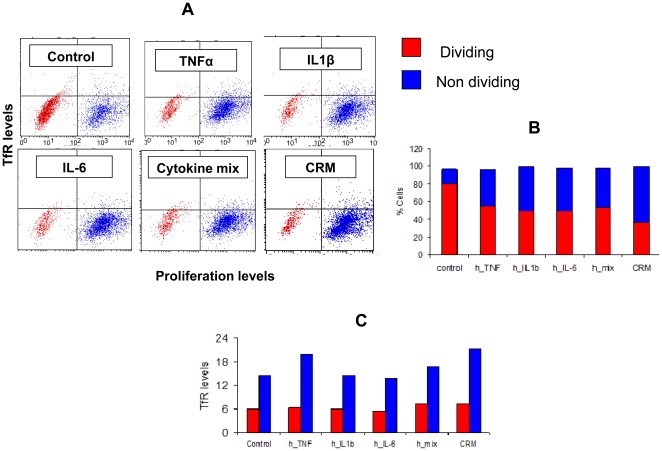
Generation of bone marrow-derived DCs and PrA treatment
- DCs were derived from the bone marrow precursors of Wistar rats as described previously 6 cells/ml in RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10 ng/ml each of rat GM-CSF and IL-4 .
- To induce DC maturation, cells at day 6 in vitro were treated for 48 h with lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 10 ng/ml, , ).
- The DC phenotype was confirmed by anti-OX62 labeling and flow cytometry using a FACS Calibur system (detailed below).
- Only those preparations with a purity >85% DCs were used for subsequent experiments.
- In other experiments, the DCs at day 6 were treated for 48 h with LPS plus different doses of PrA.
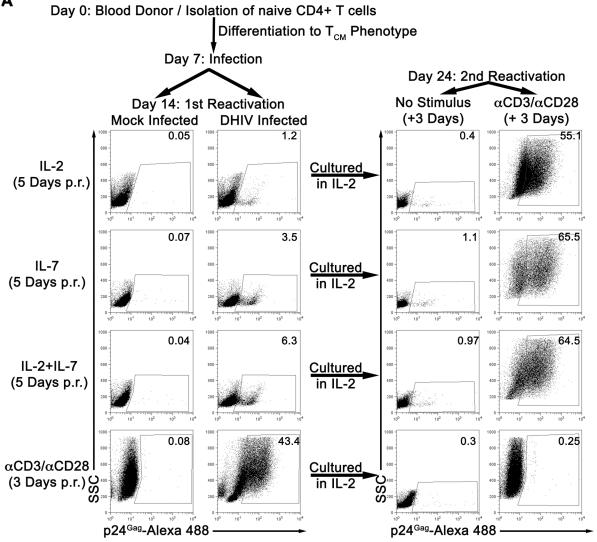
2.5. Primary splenocyte and bone marrow-derived dendritic cell (BMDC) culture
- Immature BMDCs were isolated using a protocol modified from previous publications 6 cells) were then cultured in 1 ml complete medium for 7 d in the presence of recombinant rat IL-4 (10 ng/ml, , , ) and recombinant rat granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF, 10 ng/ml, , , ).
- At day 7, immature BMDCs were resuspended in complete medium for maturation.
- Mature BMDCs (1×106 cells/well) were incubated with LPS (1 µg/ml, from
E. - coli, , , ) for 12 h and then treated with culture supernatant of
F. - prausnitzii (1 µl), sodium butyrate solution (0.005834 µmol) and denatured
F. - prausnitzii or
longum bacteria (1×106 CFU/well, BMDCs: bacteria = 1:1) at 37°C for another 12 h. PBS treated BMDCs were used as a control. - Each group treatment was repeated four times.
- The supernatant was collected and stored at −20°C.
Culture and characterization of DCs
- DCs were generated from rat bone marrow as previously described[6 cells/mL in medium'>RPMI-1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum , 2 mM glutamine, 100 μg/mL penicillin , 100 μg/mL streptomycin , 500 U/mL of recombinant rat granulocyte-macrophage colony- stimulating factor , and 500 U/mL of recombinant rat interleukin-4 .
- On days 2 and 4, half of the culture supernatant was removed and replaced with fresh medium containing recombinant rat granulocyte macrophage colony- stimulating factor and interleukin-4.
- On day 6, all the loosely adherent cells were harvested, centrifuged and counted.
- Then C6 glioma cell lysates and DCs (a ratio of 3 tumor cells to 1 DC) were incubated in fresh medium with recombinant rat granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-4 together at 37°C in 5% CO2.
- To stimulate DC maturation
in vitro , on day 8, the cultures were additionally…