Mouse Leptin Recombinant
Categories: HematopoietinsIL-6 gp130 familyRecombinant Mouse Cytokines$160.00 – $300.00
Description
Accession
P41160
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding mouse Leptin mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
MouseLeptin is generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, the molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 16 kDa. Recombinant Leptin is a monomer protein consisting of 147 amino acid residue subunits, and migrates as an approximately 16 kDa protein reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent proliferation of BAF3 cellstransfected with the long form of human leptin receptor.
Protein Sequence
MCWRPLCRFL WLWSYLSYVQ AVPIQKVQDD TKTLIKTIVT RINDISHTQS VSAKQRVTGL DFIPGLHPIL SLSKMDQTLA VYQQVLTSLP SQNVLQIAND LENLRDLLHL LAFSKSCSLP QTSGLQKPES LDGVLEASLY STEVVALSRL QGSLQDILQQ LDVSPEC
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant mouse Leptin was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered NaHCO3solution.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at2° -8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
P48356
Methods
MEA Recordings
- Murine recombinant leptin was used at a final concentration of 50 nM, being applied 1 hour before the recordings, under hypoxic or normoxic conditions, and maintained in the MEA dish for the whole recording.
- Then it was washed out and we waited 2 hours before recording the recovery.
- Paxilline was dissolved in DMSO and used at the final concentration of 1 µM
Cell culture
- Neutrophils isolated from children were cultured at 1×106 per ml in complete culture medium (PMI 1640 containing 10% FBS) in the presence and absence of 10 ng/ml rGM-CSF, and 10 µg/mL leptin for the indicated times.
- In some experiments, 1 µg/ml cycloheximide was also added.
- Blocking experiments were performed by using inhibitors SB203580 (25 µM), Wortmannin (10 µM), PDTC (5 µM), and U0126 (5 µM) in the culture as we previoulsy described
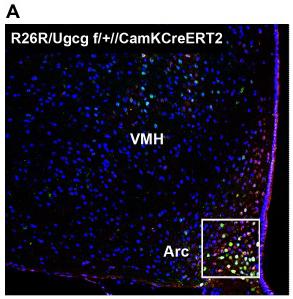
rAAV-mediated Ugcg gene delivery to the hypothalamic Arc ameliorates obesity and hyperleptinemia in Ugcg
rAAV-mediated Ugcg gene delivery to the hypothalamic Arc ameliorates obesity and hyperleptinemia in Ugcg
rAAV-mediated Ugcg gene delivery to the hypothalamic Arc ameliorates obesity and hyperleptinemia in Ugcg
Administration of leptin, MT-II, and inhibitors.
- Leptin (5 ng) , the MCR agonist MT-II (10 pmol) , or the MCR antagonist SHU9119 (10 pmol) in 0.1 µL of physiological saline was injected with a Hamilton microsyringe into the right side of the VMH of freely moving mice through the unilateral .
- The MEK inhibitor U0126 (10 μmol/L) (Cell Signaling Technology, Beverly, MA) or the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (10 μmol/L) in 0.1 µL of 0.01% DMSO was injected into the same side of the VMH at 1 h before injection of leptin or MT-II.
- Cell-permeable SH2 domain–binding phosphopeptide (STAT3 inhibitor) (0.1 µL of a 250 μmol/L solution in saline) was injected into the VMH twice, at 1 h and 5 min before leptin injection.
- In some experiments, 0.1 µL of U0126 (10 μmol/L in 0.01% DMSO) or the STAT3 inhibitor (250 μmol/L in saline) was injected into the VMH bilaterally at 1 h or at both 1 h…
Leptin administration via mini-osmotic pump.
- Recombinant murine leptin was reconstituted in water according to the manufacturer’s instructions and loaded in osmotic pumps (DURECT Corporation, , ) designed for either 4-week or 6-week infusion.
- Pumps were implanted subcutaneously on day 0.
- Diabetic vehicle-treated mice received osmotic pumps loaded with water only.
- Nondiabetic controls received sham surgery without pump implantation.
- For the leptin dosing study, the concentration of leptin loaded into the pumps was adjusted to deliver doses of 1, 3, 5, and 10 µg/day per mouse, whereas for the islet transplant study a single dose of 1 µg/day per mouse was used.
Feeding Experiments
- Mice were assigned randomly to receive i.p.
- injection of vehicle (0.9% w/v NaCl), CCK-8 sulphated (20 μg/kg , ), or recombinant murine leptin (5 mg/kg, ).
- Injections were made in a volume of 4 ml/kg body weight.
- Injections were made at lights off (2,000 hr; ZT12), and food intake was determined 1, 2, 4, and 24 hr after injection.
Whole‐cell patch‐clamp recordings
- Whole‐cell patch‐clamp recordings were performed at 34–36°C on EGFP‐positive LepRb neurons and on stomach‐related (red) LepRbEGFP neurons throughout the DMV identified under 40× water‐immersion objective (N.A = 0.8).
- Epifluorescence was used to identify EGFP and/or RFP containing neurons and infrared illumination and differential interference contrast optics (IR‐DIC) to target specific cells.
- For whole‐cell patch‐clamp recordings, electrodes (3–7 MΩ) were filled with a solution containing the following (in mmol/L): 130 K+ or Cs+ gluconate, 10 HEPES, 5 EGTA, 1 NaCl, 1 MgCl2, 1 CaCl2, 3 KOH or CsOH, 2–3 Mg‐ATP, 0.2% biocytin, pH 7.3–7.4.
- Electrophysiological signals were recorded using an Axoclamp 700B amplifier and acquired by pClamp .
- Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) were recorded at −60 mV, whereas inhibitory postsynaptic currents (IPSCs) were recorded at −10 mV without additional inhibitors.
- Synaptic currents were analyzed offline using pClamp or MiniAnalysis .
- Tetrodotoxin (TTX; 1
μ mol/L , & Systems , , ) in…