MHC peptide Complexes
Immunotherapy has become one of the most promising avenues for cancer treatment, making use of the patient’s own immune system to eliminate cancer cells. Activated T cells are capable of directly recognizing antigens that are presented on the surfaces of tumour cells.Thus emerging immuno therapy technologies are now targeting activated T cells in order to identify and kill tumor cells.
The activation of T-cell immunity is primarily driven by the interaction between peptides presented by major histocompatibility complexes (pMHCs) and T-cell receptors (TCRs).TCRs are found on the surface of T-cells where they recognize protein fragments, named antigens, when these are presented by the MHC on the cell surface of antigen presenting cells.The TCR-pMHC complex consists of two components, namely the TCR and the pMHC. The MHC class I molecule is a heterodimeric glycoprotein that consists of an α chain and a β2-microglobulin chain. The α chain is composed of three globular domains named α1, α2 and α3 which are highly polymorphic, allowing the MHC variants to accommodate a diverse range of peptides of different lengths and compositions.
we are offering various pMHC complex recombinant molecules to be used in immunotherapeutic research involving activation of T cells. These pMHC recombinants may be used in T cell screening, T cell activation in the development and characterization of tumor targeting T cells.
Browse by MHC allele

HLA-A peptide Complexes
HLA-A is a highly polymorphic gene that encodes the HLA-A protein, which is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule involved in presenting peptides to cytotoxic T cells.HLA-A has over 4,500 identified allele variants, with varying frequencies across different populations
several HLA-A alleles have been associated with an increased risk or protection against various diseases:
Autoimmune Diseases
- HLA-A*01:01 is associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis (MS)2.
- HLA-A*02:01 is protective against the development of MS, but increases the risk of autoimmune hepatitis and ankylosing spondylitis
- HLA-A*03:01 is linked to an increased risk of rheumatoid arthritis
Type 1 Diabetes
- HLA-A*24:02 is linked to a higher risk of developing type 1 diabetes
- HLA-A*11:01 is associated with a reduced risk of type 1 diabetes
Other Diseases
- HLA-A*03:01 increases the risk of primary sclerosing cholangitis
- HLA-A01:01 and HLA-A24:02 are associated with an increased risk of Behçet’s disease
- HLA-A*24:02 is linked to a higher risk of autoimmune thyroid disease
| Catalogue | Description | Species | Tag | Host | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
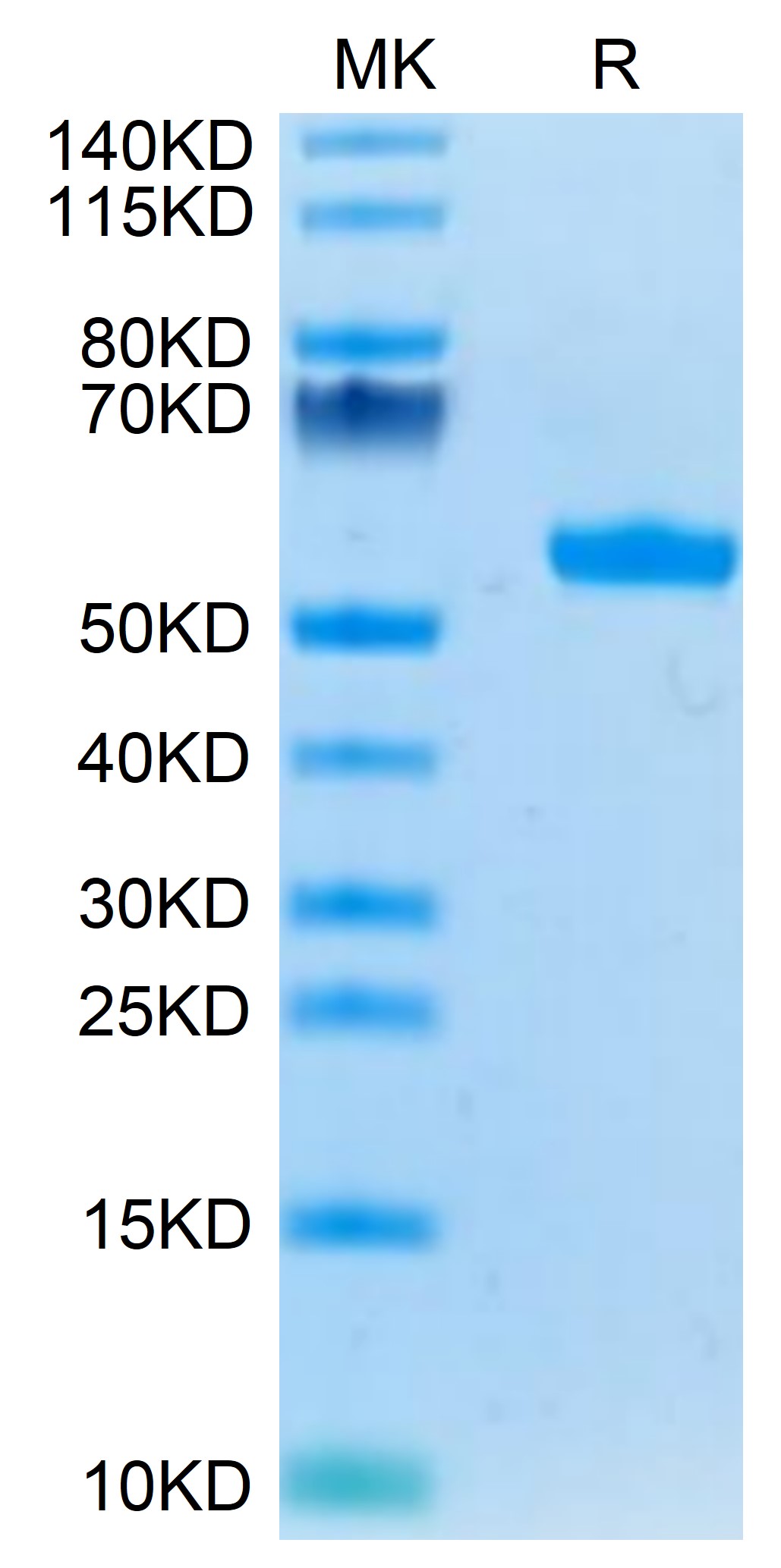
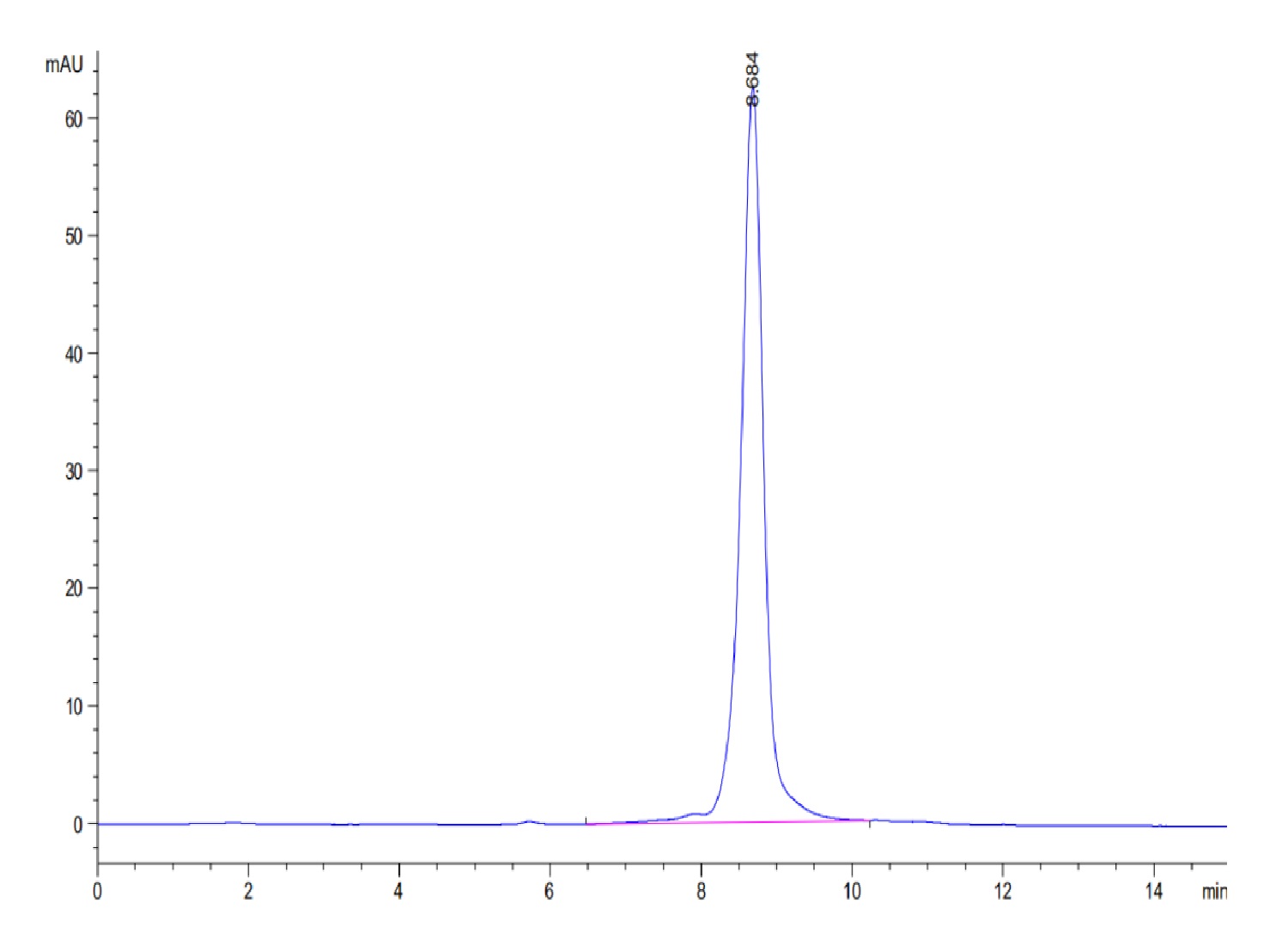
| MHCKRAS2B | Biotinylated HLA-A*011:01 KRAS G12D peptide complex | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
|
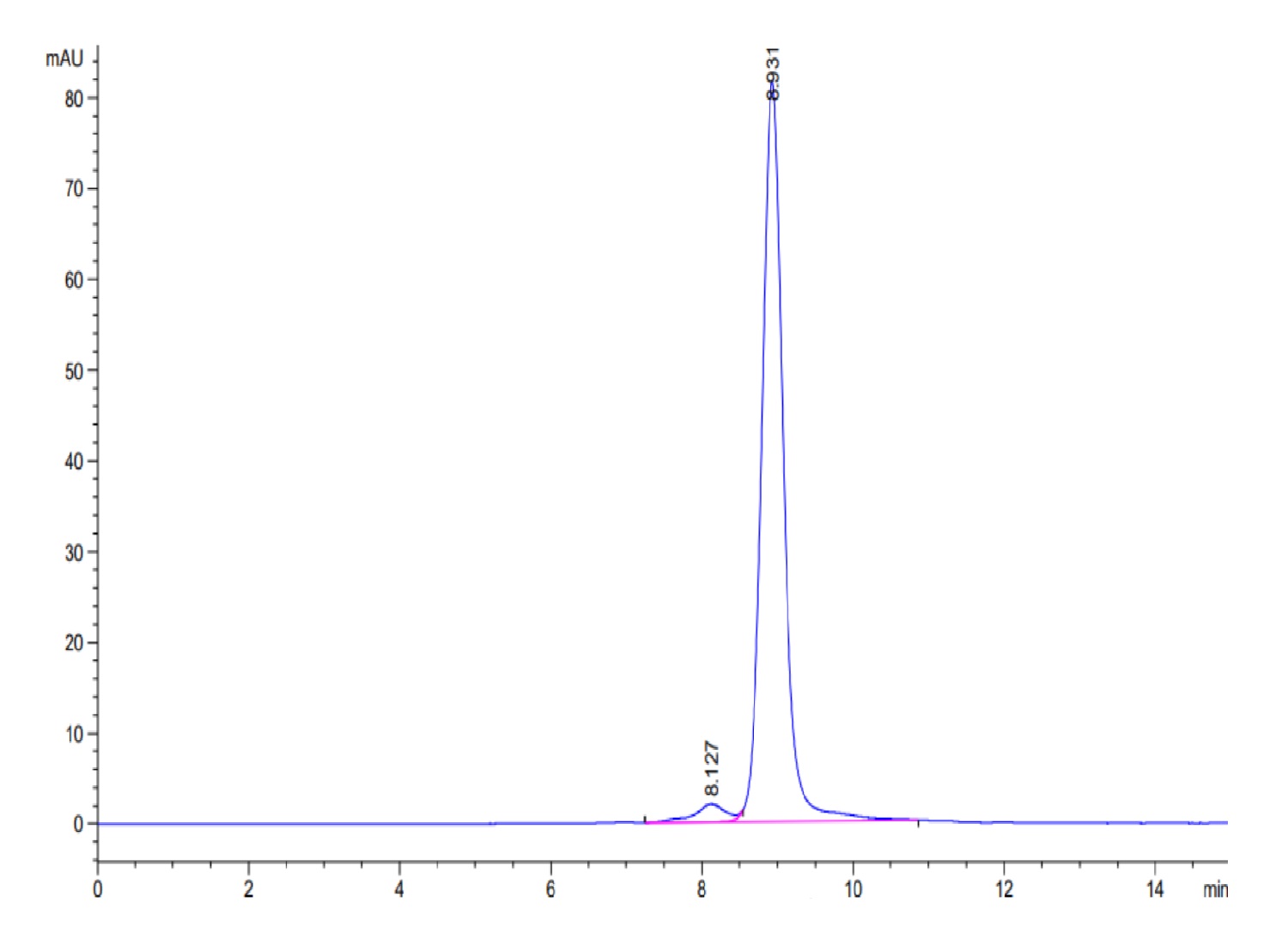
| MHCKRAS2VB | Biotinylated HLA-A*011:01 KRAS G12V peptide complex | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
|
| KTXZY65H | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 CLGGLLTMV peptide complex | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 |
|
| KTX4NOJ2 | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 FLLTRILTI peptide complex | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 |
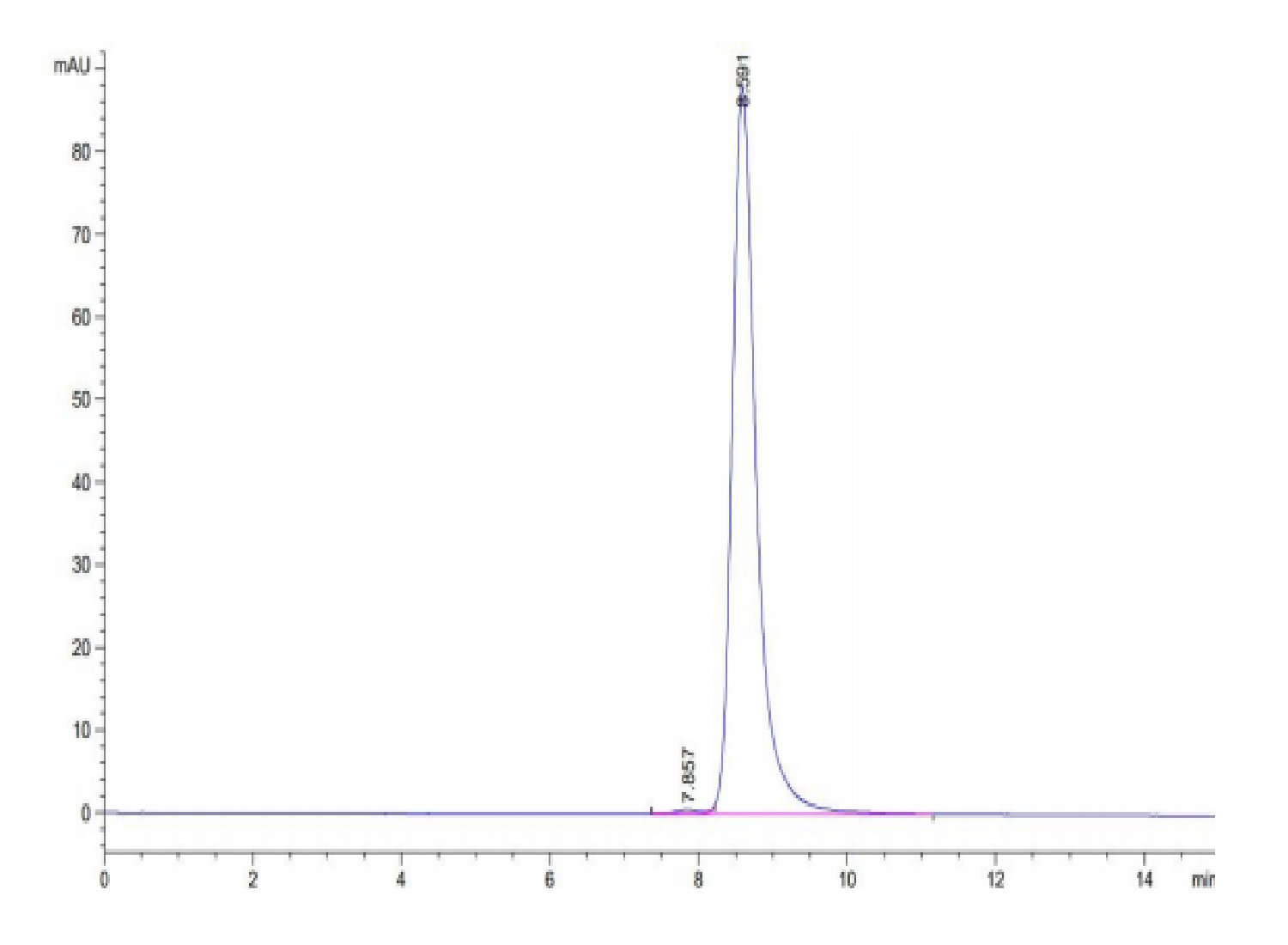
|
| KTZEF7WG | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 FMNKFIYEI peptide complex | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 |
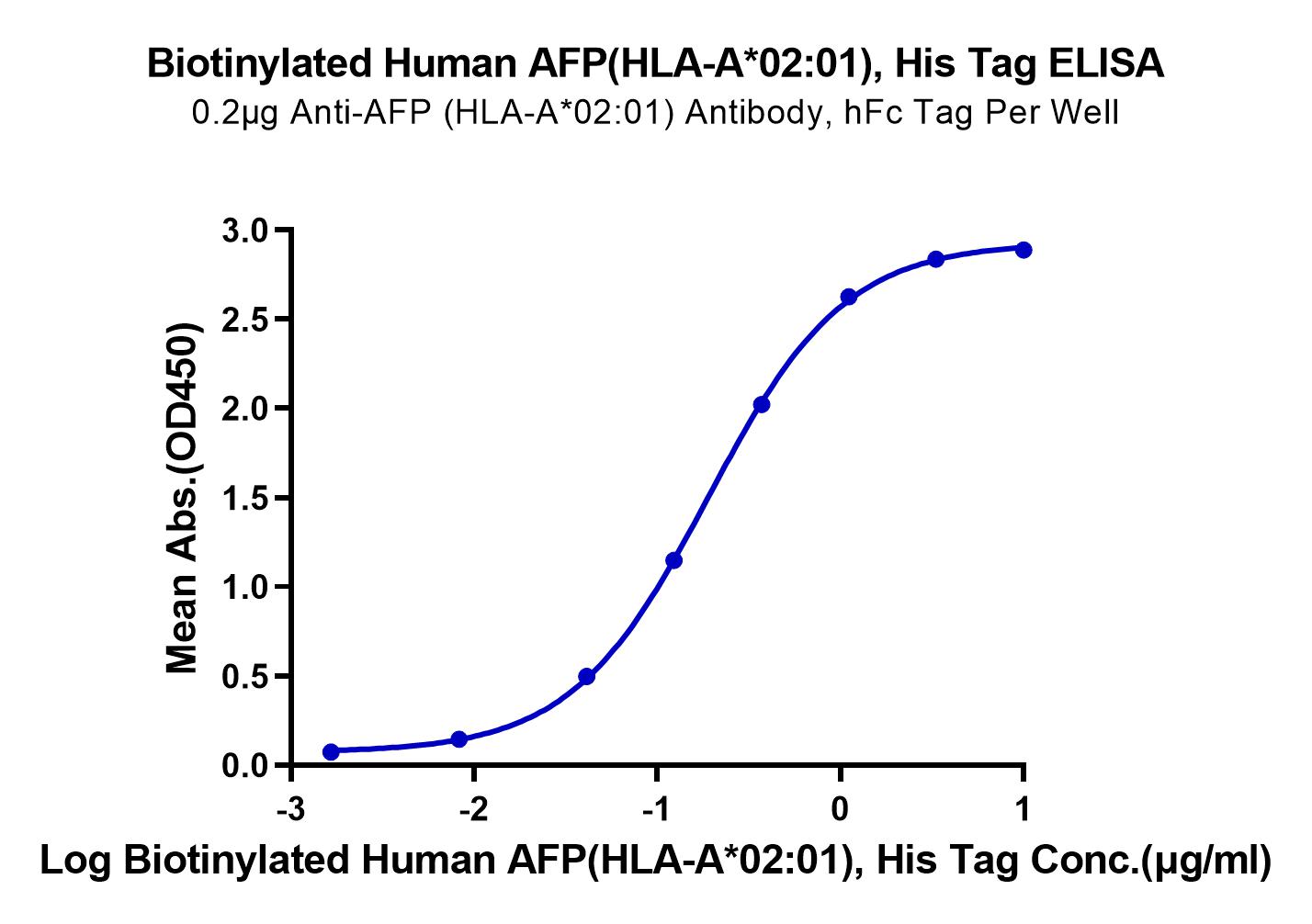
|
| KTHU62DH | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 HMTEVVRRC peptide complex | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 |
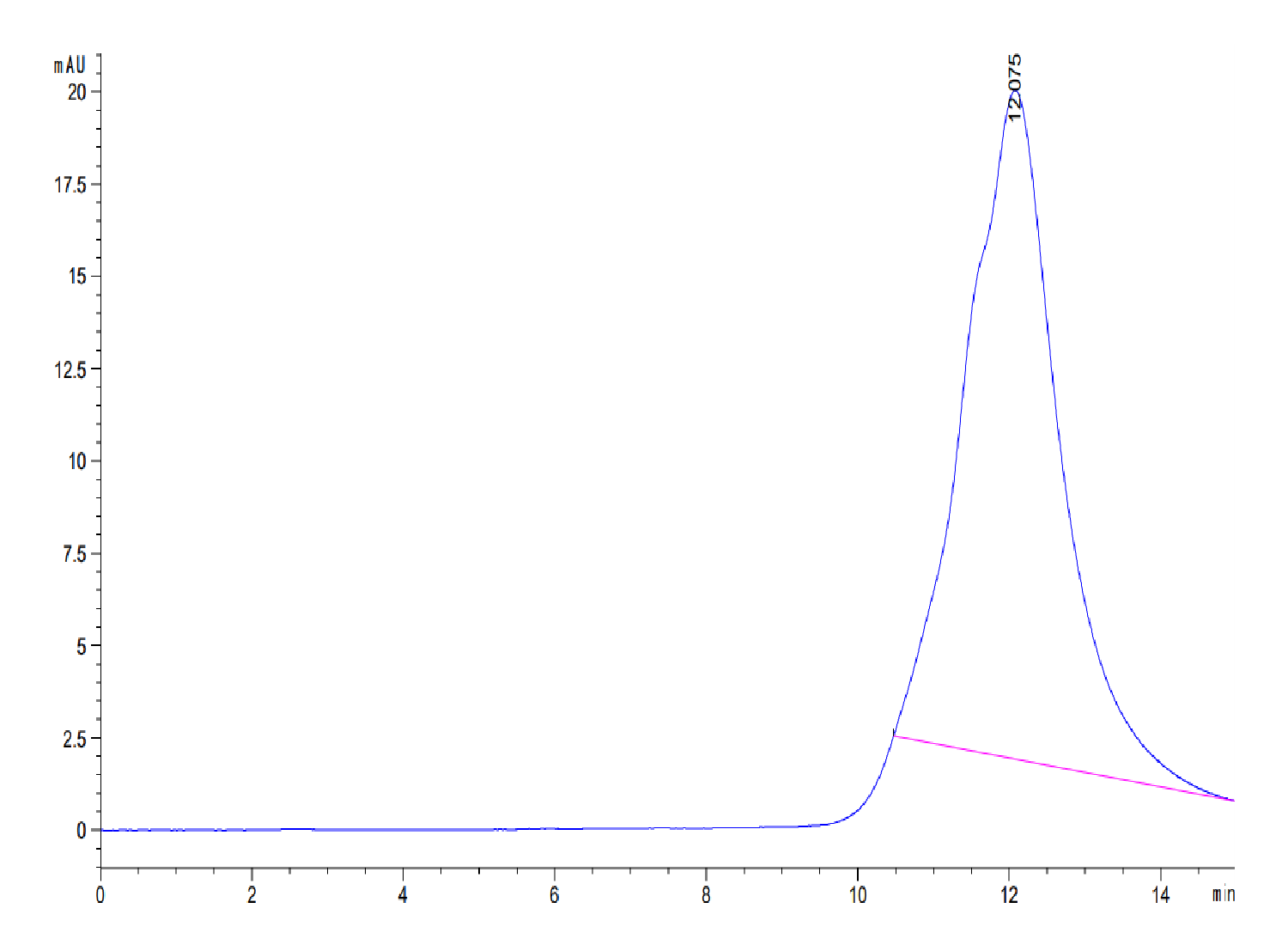
|
| KTW80VEE | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 LMLGEFLKL peptide complex | Human | C-His-Avi | HEK293 |
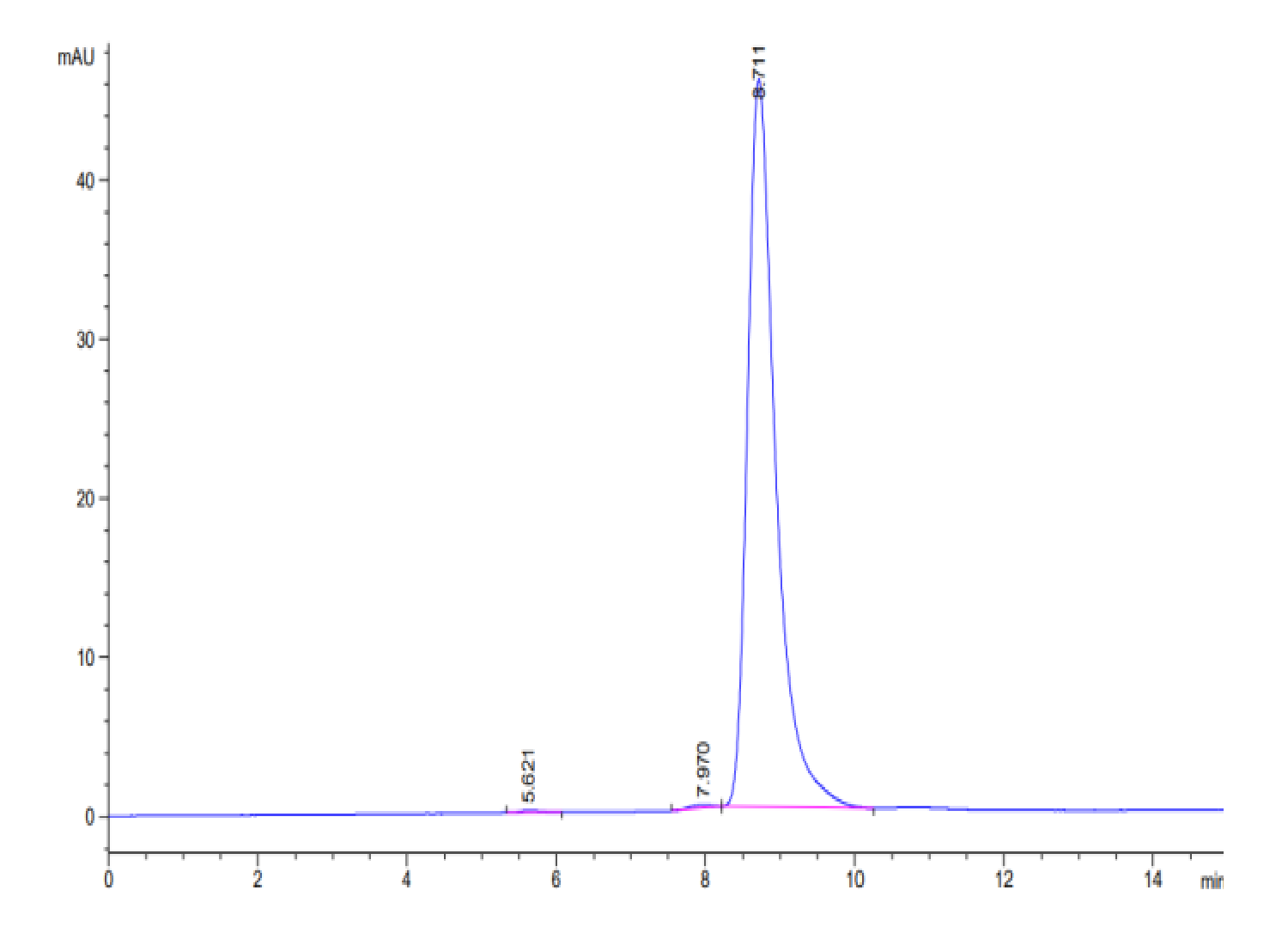
|
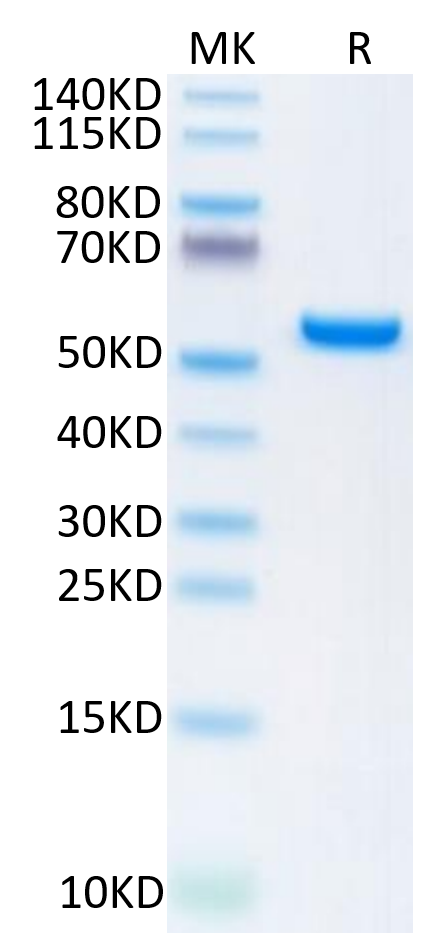
| MHCP53B | Biotinylated HLA-A*02:01 P53 R175H peptide complex | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |

|
Browse by Peptide

HLA-G peptide Complexes
The HLA-G allele refers to a specific variant of the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) gene, specifically the HLA-G gene. HLA-G is a non-classical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule, which means it plays a different role compared to classical MHC class I molecules like HLA-A, -B, and -C.
HLA-G is primarily known for its immunomodulatory properties, particularly its role in immune tolerance during pregnancy and transplantation. It is expressed in various tissues, including the placenta, thymus, and immune-privileged sites like the cornea and testis
The HLA-G gene and its expression have been associated with the following diseases:
Autoimmune Diseases
- HLA-G plays an important role in the regulation of the immune system during autoimmune conditions, such as gastrointestinal, skin, rheumatic, and neurological diseases
- Multiple sclerosis (MS): soluble HLA-G (sHLA-G) antigens may have a tolerogenic role in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis
Viral Disease
- HLA-G has been implicated in the immune-escape mechanisms
- Increased levels of soluble HLA-G have been linked to higher incidence of Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) and Visceral leishmaniasis
| Catalogue | Description | Species | Tag | Host | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biotinylated HLA-G peptide complex |
|
||||
| MHCHLAG | HLA-G peptide complex | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
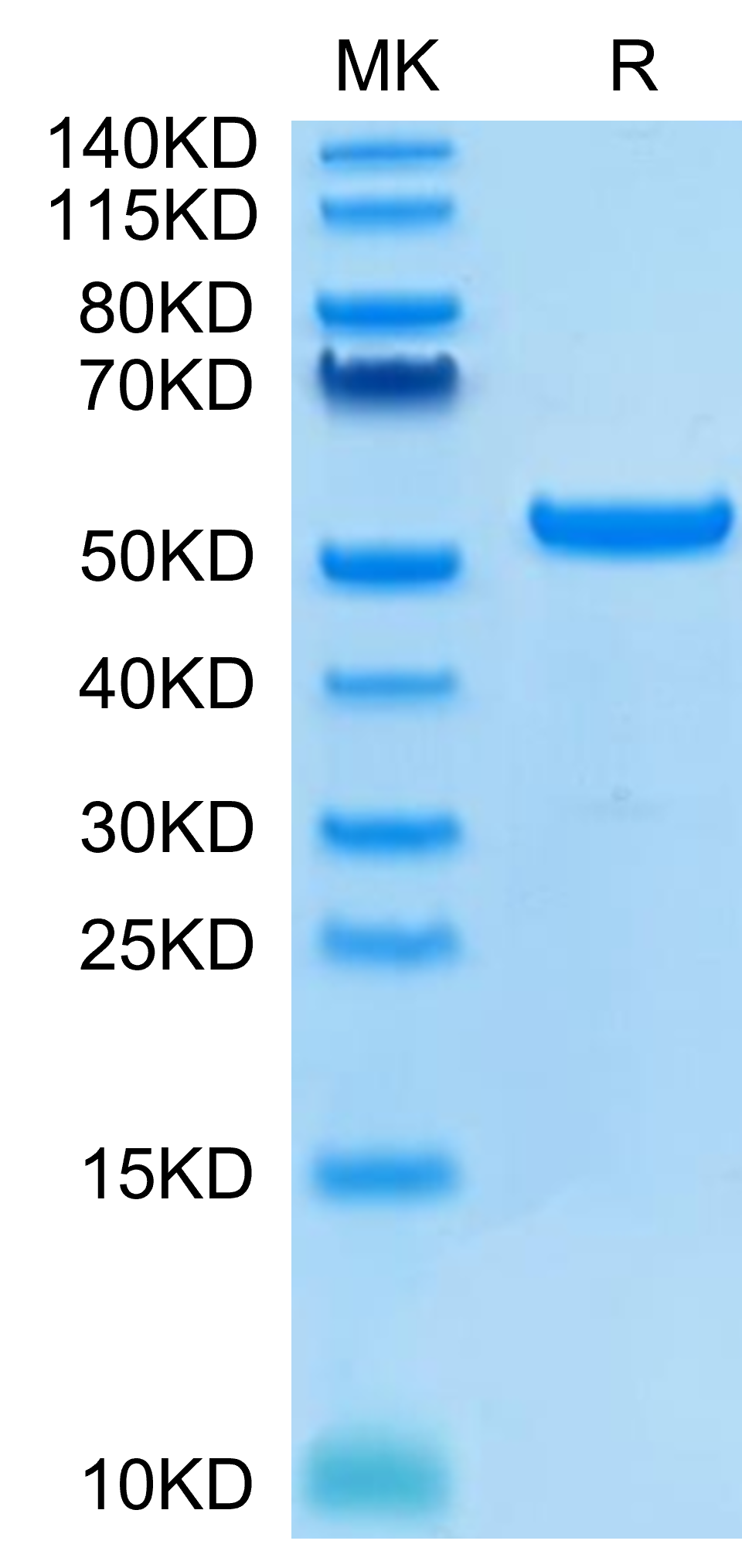
|
| MHCHLAGT | HLA-G peptide complex Tetramer | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
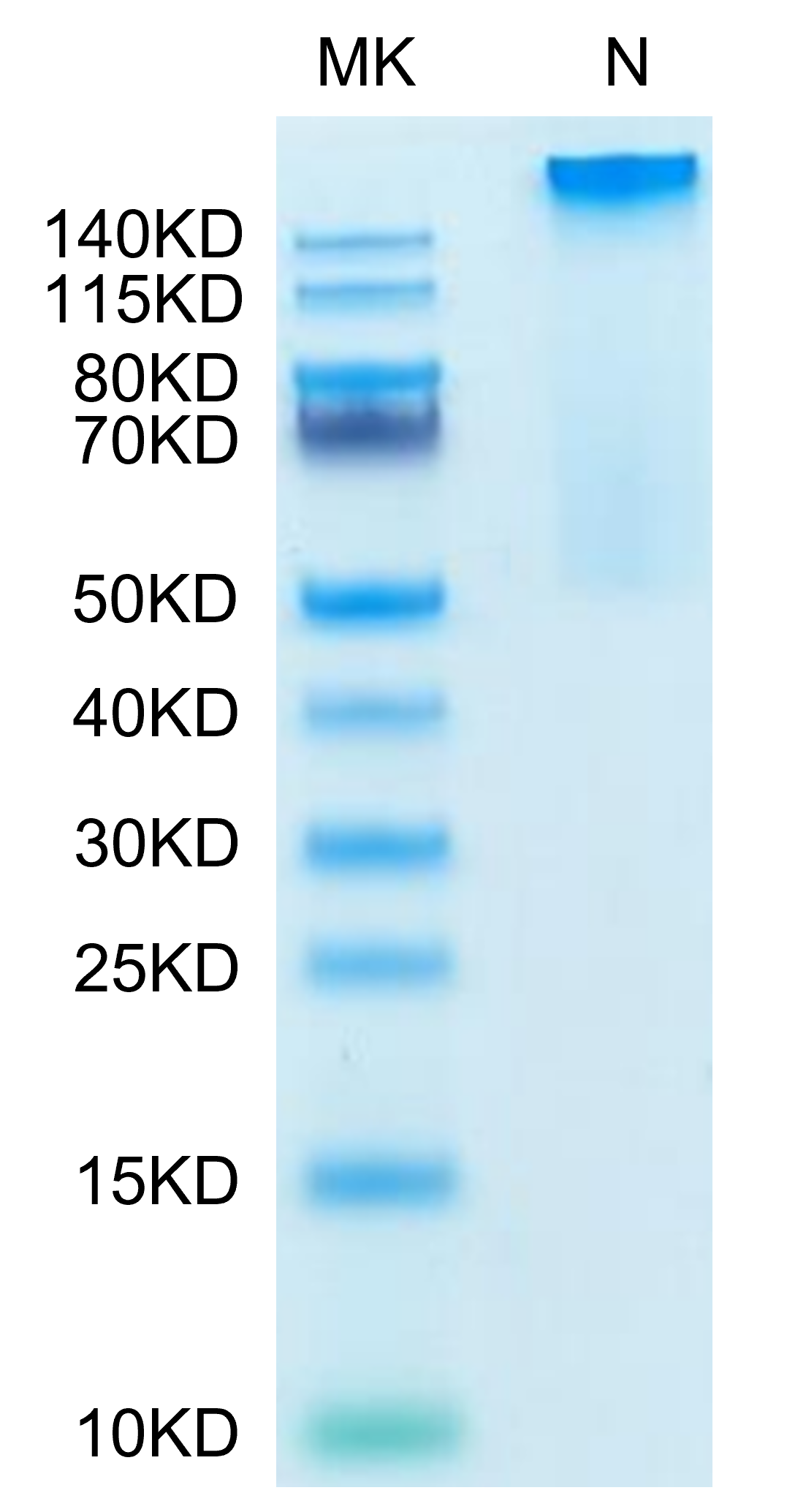
|

HLA-E peptide Complexes
HLA-E plays a role in immune regulation and immune surveillance by presenting peptides derived from other MHC class I molecules, specifically from the leader sequences of classical MHC class I molecules such as HLA-A, -B, and -C. These peptides serve as ligands for receptors on natural killer (NK) cells and subsets of T cells.One of the key functions of HLA-E is its involvement in immune surveillance against infected or stressed cells. It interacts with inhibitory receptors on NK cells, preventing their activation and subsequent killing of healthy cells displaying self-MHC molecules. However, when cells are infected or stressed, the presentation of non-self peptides on HLA-E can trigger NK cell activation and targeted killing of these abnormal cells.
The HLA-E gene and its expression have been associated with the following diseases:
Autoimmune Diseases
- HLA-E polymorphisms have been associated with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis
- HLA-E*01:01 was found to be realted to a reduced risk of Behçet’s disease
Viral Disease
- HLA-E01:01 (R allele) is associated with increased risk of HIV-1 infection, while HLA-E01:03 (G allele) confers protection against HIV-1.
- LA-E*01:03 is linked to higher risk of cytomegalovirus (HCMV) reactivation in kidney transplant recipients
- HLA-E*01:01 is correlated with hepatitis C virus (HCV) co-infection
| Catalogue | Description | Species | Tag | Host | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MHCHLAE | HLA-E*01:03 peptide complex | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
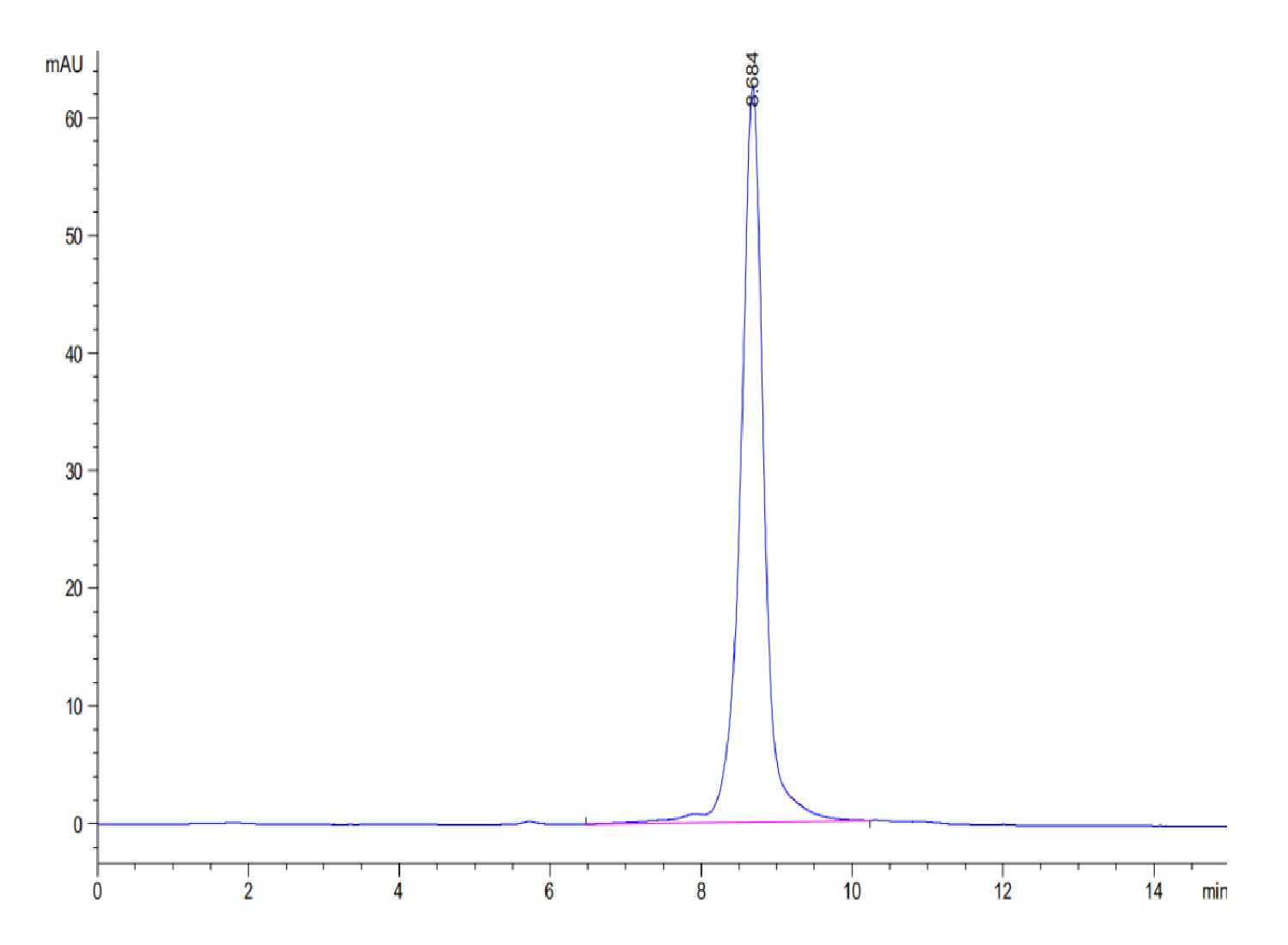
|
| MHCHLAET | HLA-E*01:03 peptide complex Tetramer | Human | His Avi | HEK293 |
|

