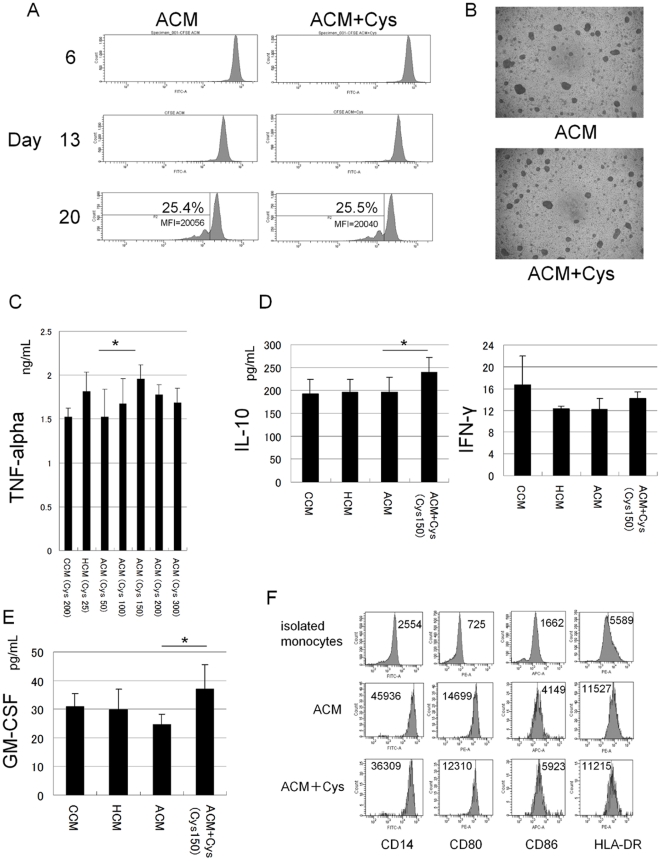
Mouse Macrophage Colony stimulating Factor Recombinant
Categories: PDGF familyPDGF familyRecombinant Mouse Cytokines$70.00 – $4,700.00
Description
Accession
P07141
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encoding mouse M-CSF extracellular domain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
Mouse MCSF, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, The molecule has a calculated molecular mass of approximately 18 kDa. Recombinant Mouse M-CSF is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein consisting of two 156 amino acid residue subunits, andmigrates as an approximately 37 kDa protein under non-reducing and as 18-19kDa under reducing conditions in SDS-PAGE.
Purity
>95%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED(50) was determined by the dose-dependent stimulation of the proliferation of of M-NFS-60 cells is < 1.0 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of > 1 x 106 units/mg.
Protein Sequence
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Recombinant mouse MCSF was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered PBS solution.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers.
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at 2° - 8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
P03228
Interactor
P03228
Interactor
Interactor
P46414
Interactor
Biological Process
Biological Process
Molecular function
Molecular function
Methods
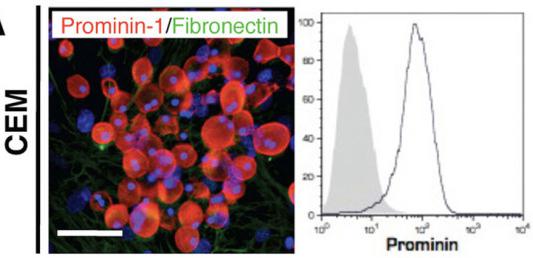
Lung-derived prominin-1.
- Exposure of prominin-1+ cells to M-CSF for 7 days resulted in formation of E.coli phagocytising F4/80-positive cells .
Osteoblast, osteoclast and macrophage differentiation.
- Bone marrow derived monocytes were seeded in 24-well culture plates and induced to differentiate into macrophages or osteoclasts via the addition of M-CSF or M-CSF + RANKL respectively.
Cell activation assay and immunodetection of cytokines
- Single spleen cell suspensions were prepared by mechanical disruption on a cell strainer (70 µm pore diameter , , ) in Dulbecco's D-PBS .
- Red blood cells were lysed using Hemolytic Gey's Solution as previously described
Osteoclastogenesis assays
- Osteoclastogenesis assays were performed as in 5 cells were plated in each well of a 24-well dish with 60 ng/mL RANKL for 3 days.
- After 3 days, 2×103 MDA-231, shControl, or shEGFR-MDA-231 cells were plated with the bone marrow cells, with 60 ng/mL RANKL and 10 ng/mL MCSF and grown for 3 days before TRAP staining.
- For TRAP staining, cells were washed with 1×PBS, fixed with ice cold methanol for 10 minutes, and stained in fresh TRAP solution for 15 minutes at 37°C.
- TRAP solution was replaced with 1×PBS for cell counting under the microscope.
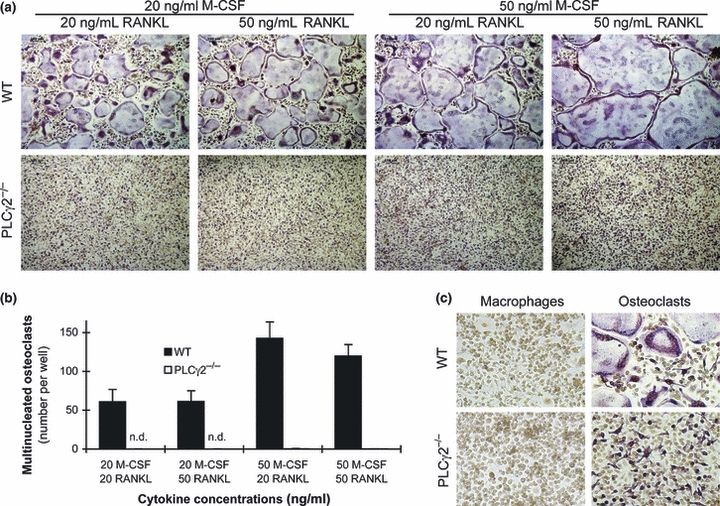
PLCγ2 is required for in vitro osteoclast development.
- (a) Representative TRAP-stained images of wild-type and PLCγ2−/− bone marrow cells cultured in the presence of the indicated concentrations of recombinant murine M-CSF and RANKL for 4 days.
Generation of bone marrow-derived macrophages
- Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM) were generated by flushing the bone marrow from the femurs of BALB/c mice with RPMI 1640 media.
- Freshly collected bone marrow cells were cultured overnight in complete media (CM; RPMI 1640, 10% fetal bovine serum [Atlanta, ], 10 mM HEPES buffer, 10 mM nonessential amino acids, 10 mM sodium pyruvate) containing 5 ng/ml recombinant murine M-CSF .
- The non-adherent cells were then collected and cultured for an additional six days in CM with 30 ng/ml M-CSF to generate macrophages.
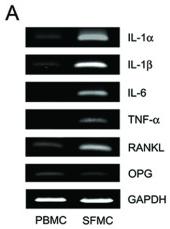
Pro-resorptive cytokine expression and osteoclastogenesis in the synovial fluid of patients with gouty arthritis.
- PBMCs, SFMCs, and T cell-depleted SFMCs (3 × 105 cells/well) were cultured for 10 days in the presence of macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF; 30 ng/ml) at the different RANKL concentrations and then were stained for tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase .
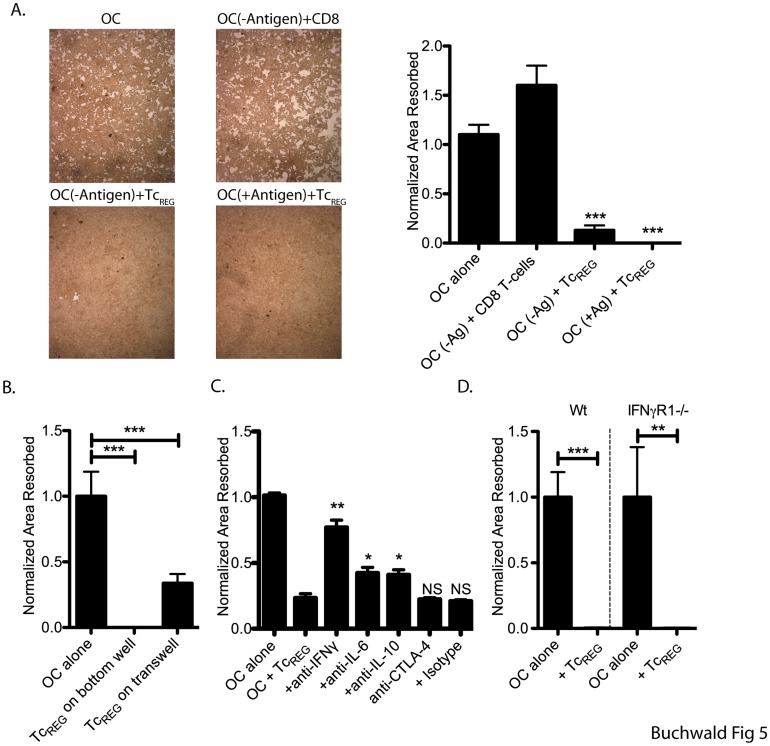
TcREG inhibit osteoclast activity in an antigen- and contact-independent manner by secreted cytokines.
- Cells were re-fed with medium containing M-CSF and RANKL every 2 to 3 days.
Induction of 2nd iPSCs
- All isolated somatic cells were cultured in the presence of Dox (2 ug/ml) for induction of 2nd iPSCs.
- Fibroblasts and hematopoietic cells were cultured in ES/iPSC medium.
- FLCD45 were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml human TPO, 10 ng/ml mouse EPO, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-3, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-6, 10 ng/ml mouse Flt3 ligand, 10 ng/ml mouse GM-CSF, 10 ng/ml mouse VEGF and 50 ng/ml mouse SCF .
- HSCs, HPCs and MPs were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml human TPO, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-3, 10 ng/ml mouse IL-6 and 10 ng/ml mouse Flt3 ligand .
- Macrophages were cultured in the presence of 5 ng/ml M-CSF .