Mouse Epidermal Growth Factor Recombinant
Category: Recombinant Mouse Cytokines$70.00 – $230.00
Description
Accession
P01132
Source
Optimized DNA sequence encodingMouse EGF mature chain was expressed in Escherichia Coli.
Molecular weight
RecombinantMouse EGF, generated by the proteolytic removal of the signal peptide and propeptide, is a monomer protein. Recombinant Mouse EGF consists of 54 amino acidsandmigrates as an approximately6.2 kDa protein under reducing conditions.
Purity
>97%, as determined by SDS-PAGE and HPLC
Biological Activity
The ED50 was determined by a cell proliferation assay using balb/c 3T3 cells is ≤ 0.1 ng/ml, corresponding to a specific activity of ≥ 1 x 107 units/mg.
Protein Sequence
970 980 990 1000 1010 1020 STAPSLLGED GHHLDRNSYP GCPSSYDGYC LNGGVCMHIE SLDSYTCNCV IGYSGDRCQT 1030 1040 1050 1060 1070 1080 RDLRWWELR H AGYGQKHDIM VVAVCMVALV LLLLLGMWGT YYYRTRKQLS NPPKNPCDEP
Endotoxin
Endotoxin content was assayed using a LAL gel clot method. Endotoxin level was found to be less than 0.1 ng/µg(1EU/µg).
Presentation
Mouse EGF was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.5.
Reconstitution
A quick spin of the vial followed by reconstitution in distilled water to a concentration not less than 0.1 mg/mL. This solution can then be diluted into other buffers
Storage
The lyophilized protein is stable for at least 2 years from date of receipt at -20° C. Upon reconstitution, this cytokine can be stored in working aliquots at 2° - 8° C for one month, or at -20° C for six months, with a carrier protein without detectable loss of activity. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Usage
This cytokine product is for research purposes only.It may not be used for therapeutics or diagnostic purposes.
Interactor
Interactor
Molecular function
Methods
Cell Culture
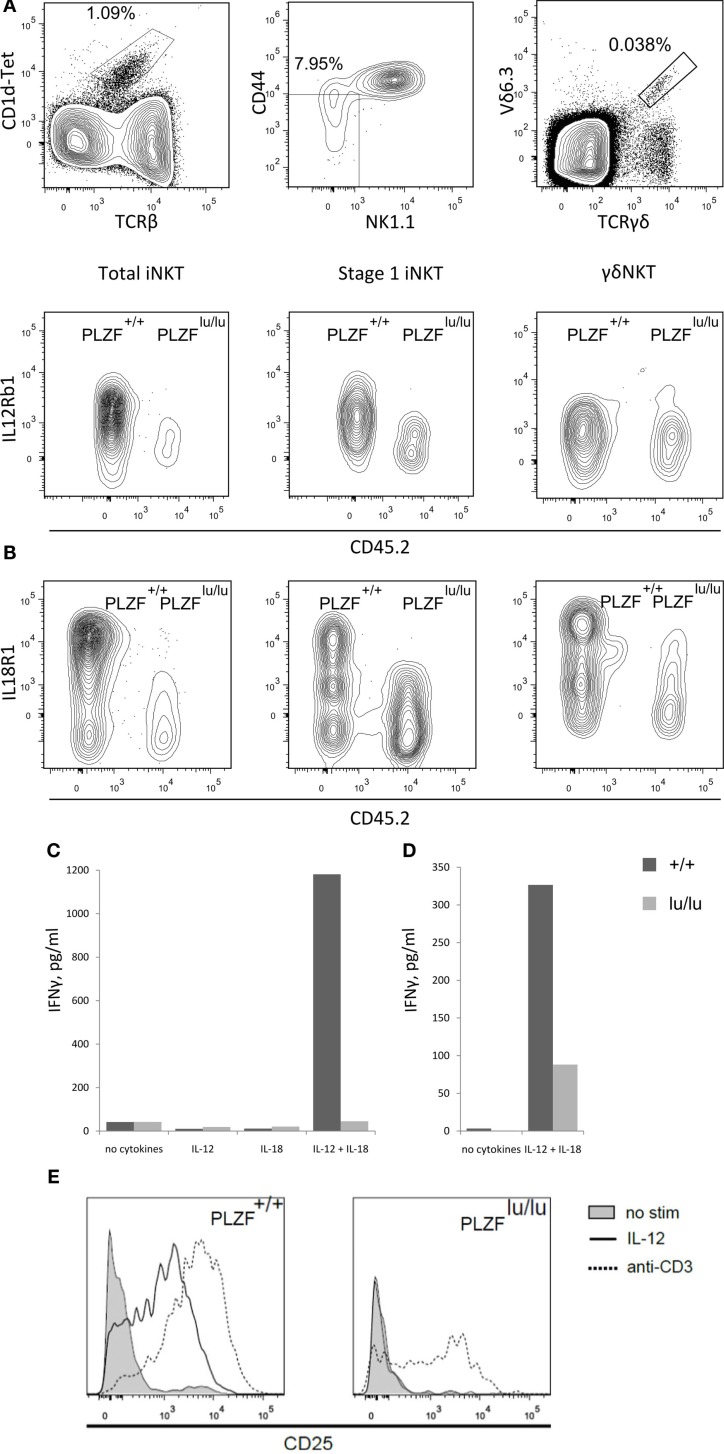
- Mouse NS cells containing a constitutively expressed marker for green fluorescent protein (GFP) were used to investigate the process of neural differentiation.
- Primary cells were obtained from central nervous system tissue of embryonic mice, and cultured primarily as previously described 2.
- Subculture occurred at day 7 with mechanical dissociation of neurospheres.
- The differentiation of mouse NS cells
in vitro was induced by culturing dissociated cells in differentiation medium containing MEM/F12 with 1× N-2 supplement, 100 ng/ml bFGF, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) , 500 nM all-trans retinoic acid , 50 µM taurine , 10 ng/ml transforming growth factor-β2 (TGF-β2) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin in tissue culture plates pre-coated with poly--lysine . - The culture medium was changed every 3 days.
- Differentiated cells at 5×105 cells/ml were processed for immunobloting assays.
- Transfections and cell treatments were carried out at 2.5×105 cells/ml cellular density.
Hepatocyte isolation and culture
- Hepatocytes were isolated from the whole liver of an adult ICR mouse (male, 7–8 weeks old) by the two-step liver perfusion method of45 H2O , 50 pM ZnSO47 H2O
Tissue culture
- Tumors derived from mice deficient in both p53 and patched were kindly provided by Dr. James A. Waschek at UCLA
Neurosphere culture
- Neurospheres were generated from cells isolated from the subventricular zone of 6–8 week old C57BL/6 mice and cultured in proliferation media consisting of DMEM/F12 (GibcoBRL/Invitrogen) containing 0.6% glucose, 3 mM NaHCO3, 5 mM HEPES, 2 mM L-glutamine, 0.1 mg/ml apo-transferrin, 25 µg/ml insulin, 60 µM putrescene, 30 mM sodium selenite, 20 nM progesterone and 1% BSA (all from), supplemented with EGF (20 ng/ml) and FGF2 (10 ng/ml), as previously described
Neurosphere cultures
- Neurosphere (NS) cultures were derived from adult mice (∼ four month-old).
- Briefly, 4 mice per culture were decapitated, brains removed and the hippocampus and subventricular zone were dissected, minced and dissociated with DMEM containing glutamine, gentamicin and fungizone.
- After treatment with trypsin-EDTA, hialuronidase and DNAse, myelin was removed by using DPBS .
- Cells were seeded into six-well dishes and cultured in DMEM:F12 (1∶1) containing 20 ng/ml epidermal growth factor , 20 ng/ml fibroblast growth factor (FGF, ) and B27 medium .
- After ∼10 days in culture, some NS were centrifuged five min at 1000× g, washed with phosphate-buffered-saline and protein was extracted in RIPA buffer.
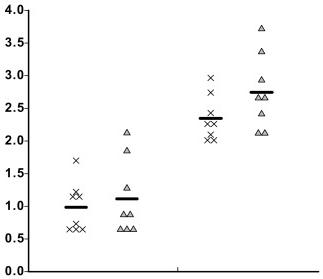
- Twenty µg of total protein was loaded on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and western blot analysis to detect C/EBPβ was performed as previously described
C/EBPβ andC/EBPβ to produce neurons, NS from 10-day old cultures were plated for 72…
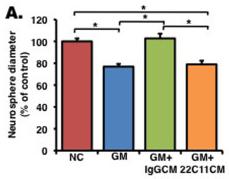
Soluble amyloid precursor protein alpha (sAPPα) enhances proliferation in an EGF/bFGF-independent manner.
- (b) A neurosphere formation assay was performed without growth factors (EGF and bFGF), and NPCs were treated with an inactive inhibitor , GM6001 , or GM6001 + recombinant sAPPα (GM+rec sAPPα).
Isolation of intestinal crypts
- Tissue was removed from PBS solution and washed multiple times with ice-cold PBS washes until the solution remained clear.
- The specimen was then placed in a Petri dish containing PBS on ice with the mucosal surface facing upward.
- Using a razor blade, excess mucoid material was scrapped from the epithelial surface.
- The specimen was then divided into approximately 0.5 cm2 pieces.
- These pieces were placed into a 2.5 mmol/L EDTA solution in PBS for 30 minutes of incubation with gentle shaking at 4°C.
- After this incubation period, the fragments were allowed to settle and the supernatant was discarded.
- 10 ml of cold PBS was added to the sample, and subsequently vortexed for 10 seconds with 1-second bursts.
- The fragments were allowed to settle, and the supernatant was removed and saved on ice.
- Again 10 ml of PBS were added and the process was repeated eight times.
- Samples were spun down at 100 g for 2 minutes.
- The supernatant…
Cell culture
-
Hepatic stellate cells, Kupffer cells and endothelial cells were isolated from Mx-conditional knockout mice (Mx-cKO) which carry the Mx-promoter attached to cre and are homozygous for the floxed fibronectin gene
in vivo prior to cell isolation as described 1 (1-10 ng/ml), murine platelet derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) (100 ng/ml) (Sigma-Adrich) or murine epidermal growth factor (EGF) (100 ng/ml) . - The TGF-β signaling inhibitor (SB431542) was used at a final concentration of 10 µM 1, PDGF-BB or EGF lasted for 24 hours or as described in the figure legends, and treatment with the inhibitor lasted one hour, after which TGF-β was added and left for an additional 2 hours before collecting the samples.
- Fibronectin used for coating was isolated from outdated human plasma as described
Pancreatic Cell Culture
- Digested pancreatic cells were seeded on a gelatin-coated 6-well plate at 5×104 cells/cm2.
- Our standard culture medium is a 1∶1 mixture of medium'>Dulbecco's medium'>modified medium'>Eagle's medium and F-12 with 5% fetal bovine serum , Nicotinamide (10 µmol/l), β-mercaptoethenol (50 µmol/l), HEPES (5 mmol/l), and Gentamycin (50 µg/ml).
- At 24 h after seeding, the medium was changed to the standard medium supplemented with epidermal growth factor (EGF) (20 ng/ml), glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 (10 ng/ml), and γ-insulin (10 µM).
- At day 12 of culture, cultured cells were used for RT-PCR analysis, histological analysis, and transplantation.
- For the histological analysis of frozen sections and transplantation, cultured cells were detached from the culture dish by pipetting with 2 mg/ml collagenase type V/PBS, taking care not to disrupt the 3D structure of islets and ducts formed
in vitro .